Religion in Ancient Rome
Romans considered religion to be very important within their daily life. Religion in Ancient Rome focused on the gods and many events were explained by somehow involving the gods. The people of Rome believed that the gods ruled their lives and so spent much of their time in worship of them.
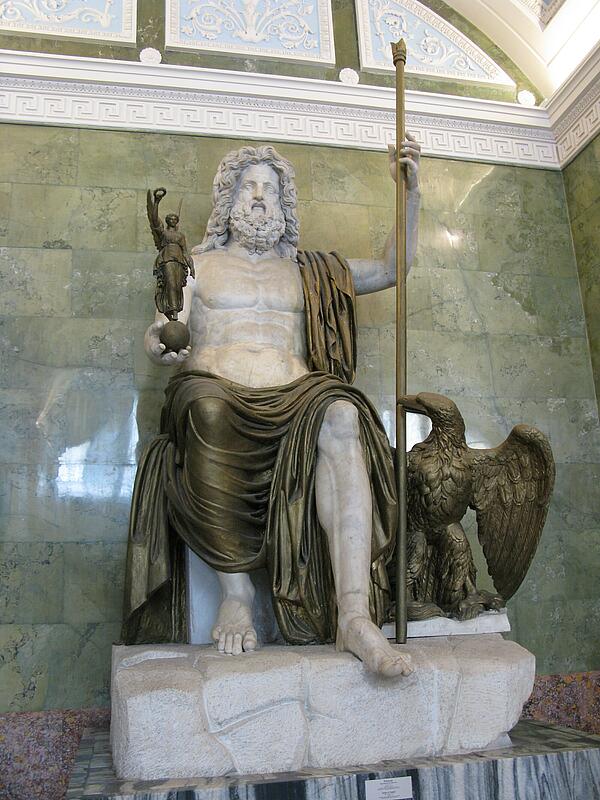
Jupiter was seen as the greatest god as he ruled the rest with his wife Juno (goddess of the sky). Among the other main gods were Mars the god of war, Neptune (god of the sea) Mercury (messenger of the gods) Janus (god of the doorway) Diana (goddess of hunting) Vesta (god of the hearth) Minerva (goddess of healing and wisdom) and Venus the goddess of love.
In early Roman religion, beliefs also included the inhabitants of spirits and that people were watched over by the spirits of their ancestors. The emperor was seen as a god after the reign of Augustus in AD 14, and he received worship on special occasions. The gods each had their own unique festival day and this was made into a public holiday. People would be able to pay visits to the temple for the god that was being celebrated, and animals would be presented as sacrifices by the priests.

Temples were built within Rome for worship of the gods, and individual family homes would all display a small altar and shrine. Each household had their own personal gods, known as ‘lares’ - these were worshipped each day, and the family’s head would lead prayers around the shrine. Family slaves were even invited as the service was thought of as extremely important. Romans were believed to have been more interested in impressing their own gods than the main public gods.
"In a corner at the entrance to the house was a huge cupboard with a small built-in shrine. Inside the shrine were the silver statuettes of the household gods, a Venus in marble and a golden casket."
Description of a family altar to the household gods, AD 60
As the empire expanded, the Romans did not force their own religious beliefs onto countries they had conquered, but they did not tolerate certain religions such as Judaism and Christianity.
Though all Roman gods would eventually be replaced by Christianity, which was viewed by some as the decline of the western empire.
Despite this, religion would always remain a central part of Roman society.
See also:
MLA Citation/Reference
"Religion in Ancient Rome". HistoryLearning.com. 2025. Web.