World War Two 1943
The year 1943 marked a shift in the successes of both sides during World War Two. As Allied forces strengthened and began to target the opposition more efficiently, they began to enjoy more frequent, consistent and notable gains, ultimately leading to the downfall of Italy before the year drew to a close.
Although both sides suffered losses, the Axis defeats were often so significant that they left Germany struggling to keep an upper hand, particularly after the Kingdom of Italy surrendered in September 1943. This specific event forced the Nazis to deliver supplies and troops south in a bid to prevent an attack on Berlin, which impacted on the nation's ability to ensure continued strength in the East and West of Europe.
Other notable defeats for the Axis forces include the D-Day landings, where Allied forces struck against the Germans in Normandy and rendered their France-based U-boat bases inoperable. This marked the biggest invasion by sea in history and was the start of Operation Overlord, which would eventually see the Allied forces arrive in Berlin and end the war. Additionally, the year of 1943 marked a turning point in the US bid to retake many of the territories taken by Japan the previous year.
See also:
World War Two 1944

| 1943 | Event |
|---|---|
| 4 January | Operation Koltso (Ring) was approved by STAVKA (the high command of the armed forces in the Soviet Union). This consisted of the German 6th Army’s being destroyed at Stalingrad unit by unit on 10 January. |
| 8 January | STAVKA requested that Friedrich Paulus, commander of the 6th Army at Stalingrad would surrender - however Paulus refused. |
| 10 January | Operation Ring started from 8am with a huge artillery attack on the 6th Army. The German troops in Stalingrad were sought out unit by unit as planned. |
| 12 January | Leningrad managed to gain a rail line and linked it to the outside. |
| 13 January | The Kharkov struggle started happening again - two Soviet armies launched an attack on the Germans there. |
| 14 January | The Casablanca conference of Allied leaders started. Winston Churchill and Franklin D. Roosevelt attended. |
| 22 January | The Germans evacuated Tripoli in Libya, and the British captured the city on 23 January. |
| 31 January | Friedrich Paulus surrendered at Stalingrad. The German 6th Army’s final surrender happened on 2 February. |
| 2 February | The first Allied merchant ship unloaded its cargo in Tripoli and this vastly improved Montgomery's supply lines. |
| 5 February | The Americans drove the Japanese out of Guadalcanal. |
| 8 February | The Russians retook the city of Kursk. |
| 9 February | Guadalcanal was taken by American forces. |
| 14 February | British General Orde Wingate’s ‘Chindits’ began their first long-range penetration patrols. |
| 16 February | The Russians retook Kharkov. |
| 20 February | The Germans set a counter-offensive against the Russians, led by Erich von Manstein. |
| 2 March | The Germans completely damaged the Russian 3rd Tank Army. |
| 3 March | Manstein massed four Panzer corps south-west of Kharkov to inflict another huge attack on the Russians. |
| 15 March | The Germans re-captured Kharkov. |
| 31 March | A ‘spring thaw’ in the weather meant Manstein was unable to make any more gains. However, in five weeks, Manstein succeeded in driving the Russians back 100 miles on the south-eastern Russian front. |
| 13 April | The Katyn Forest massacre was originally broadcast on Radio Berlin. This was a number of executions carried out in Poland, 1940, by the Soviet NKVD. The Germans found mass graves and in 1943 Joseph Goebbels chose to use the discoveries as anti-Bolshevik propaganda. |
| 19 April | The Warsaw Ghetto Uprising began. |
| 13 May | The German Afrika Korps and Italian troops in North Africa surrendered to the Allies. |
| 5 June | The German attempt to sever the Kursk salient, known as Operation Citadel began. |
| 9 July | Operation Husky was launched - the Allied invasion of Sicily. |
| 12 July | The 'greatest' tank battle in history occurred at Kursk. |
| 16 July | The Germans started retreating from the Kursk salient. |
| 17 July | Allied planes bombed the Italian mainland and Sicily. |
| 24 July | The Grand Council of Fascism came to an agreement that Italy’s military power should lie with the king - Victor Emmanuel. The RAF and USAAF air attack on Hamburg, Operation Gomorrah, began. The Operation lasted eight days and caused so much destruction that it was later given the label ‘Hiroshima of Germany’. More than 40,000 people died and around 37,000 were wounded. |
| 25 July | Mussolini was arrested. |
| 3 August | Italy made the first step in the direction of a peace settlement with the Allies. |
| 6 August | German troops started moving into Italy to increase the likelihood of a peace settlement which would remove the Italians from the war. |
| 22 August | The Germans started moving away from Kharkov and the Russians ventured into the city the following day. |
| 26 August | The Russians campaign to liberate eastern Ukraine began. |
| 3 September | Invasion of Italy by Britain and America. |
| 8 September | American/British forces landed at Salerno. |
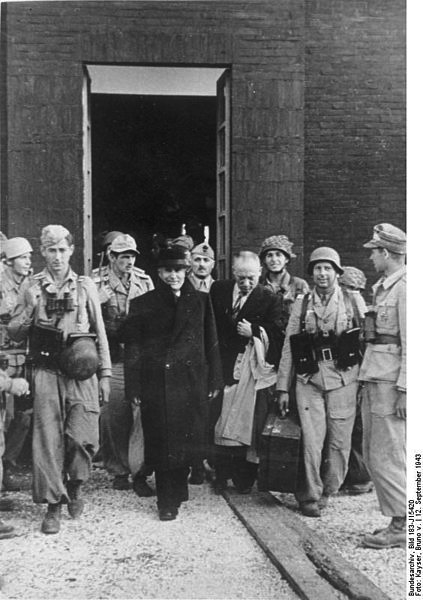
| 12 September | The Waffen-SS commandos launched the Gran Sasso raid to rescue Benito Mussolini from the Campo Imperatore Hotel in the Apennine Mountains - this turned out to be successful. |
| 25 September | Smolensk was set free. |
| 1 October | British troops entered Naples. |
| 9 October | Northern Caucasus’ liberation was finalised. |
| 6 November | German troops were made to leave Kiev. |
| 20 November | The Battle of Tarawa began, and ended with the deaths of more than 1,000 US Marines. |
| 23 November | Japan was driven out of the Gilbert Islands. |
| 28 November | The Tehran conference began. |
| 26 December | 'Scharnhorst' got sunk in the north of Norway. |
See also: World War Two 1944
MLA Citation/Reference
"World War Two 1943". HistoryLearning.com. 2026. Web.