World War Two 1941
Two fo the biggest turning points of World War Two took place in the year 1941: the Germans turned their attention towards the Soviet Union, opening its 'Second Front', and Japan attacked Pearl Harbour. The lack of firepower and manpower meant the real impact of these events wasn't truly felt until 1943, but they still spurred on two very patriotic nations that had previously avoided using their full military force against the Axis.
During 1941, however, there were huge successes in the firm of codebreaking. Throughout the year, Allied codebreakers managed to intercept a huge number of coded messages, including a number concerning Greece. This provided the Allied forces with enough time to prepare their defenses. Although the forces could not prevent Greece falling under German rule, codebreaking was a strategy that would eventually prove critical to the Allied nations. This was also aided by the recovery of the first Enigma code machine in May, after which British codebreakers set about trying to crack the Enigma code.
See also:
World War Two 1944

| 1941 | Event |
|---|---|
| January | The UK introduced clothes rationing was introduced in the UK. |
| 3 January | Italy launched their first of 46 counter-offensives in Albania against Greece, but they repulsed all of them. |
| 22 January | British and Australian forces captured Tobruk in North Africa. |
| 29 January | South African forces entered Italian Somaliland. |
| 4 February | The British encircled the Italians to the south of Benghazi. |
| 6 February | British and Australian forces ventured into Benghazi. Rommel was made commander of the German Afrika Corps. |
| 10 February | Mussolini agreed to Hitler's offer of supplying a German armoured division to Italian forces in North Africa. |
| 12 February | Erwin Rommel arrived in Tripoli. |
| 14 February | The first German units arrived in Tripoli. |
| 22 February | Anthony Eden travelled to Athens to discuss the possibility of a German attack on Greece. |
| 24 February | German and British forces clashed for the first time in the Western Desert. |
| 2 March | German troops entered Bulgaria. |
| 6 March | Ethiopia was invaded by British forces. The Germans placed magnetic and acoustic mines in the Suez Canal, leading to a three week blockage. |
| 9 March | Italy launched a huge yet unsuccessful attack on the Greeks. |
| 4 April | The Germans captured Benghazi. |
| 6 April | Germany attacked Yugoslavia and Greece. British forces occupied Addis Ababa in Ethiopia. |
| 10 April | The Germans failed to capture Tobruk; leading to the city siege. Zagreb was taken by Germany. |
| 12 April | Germany accepted the surrender of Belgrade. |
| 17 April | The Yugoslavian Army surrendered. |
| 10 May | Britain experienced the remainder of Germany’s heavy air raids, meaning the Blitz reached an end. |
| 24 May | HMS Hood lost 1,416 men out of a crew of 1,419 when it was sunk by the Bismarck. |
| 27 May | The Bismarck was sunk by the Royal Navy. Only a little more than 100 survived out of a crew of 2,200. |
| 22 June | Operation Barbarossa was first launched - also known as Nazi Germany’s invasion of the USSR. |
| 1 September | The first German shell landed in Leningrad, beginning a 900 day siege. |
| 27 September | Italian forces surrendered at the Wolchefit Pass, Ethiopia. |
| 28 September | The first Allied convoy to the USSR took place. |
| 2 October | The attack on Moscow took place - Nazi Germany’s final phase of its USSR invasion. |
| 6 October | Stalin received a promise from Churchill that a convoy would sail to Russia every 10 days. |
| 28 November | Mussolini’s East African venture was finished by Italian forces surrendering at Gondar. |
| 5 December | The Russian counter-attack in Moscow began. |
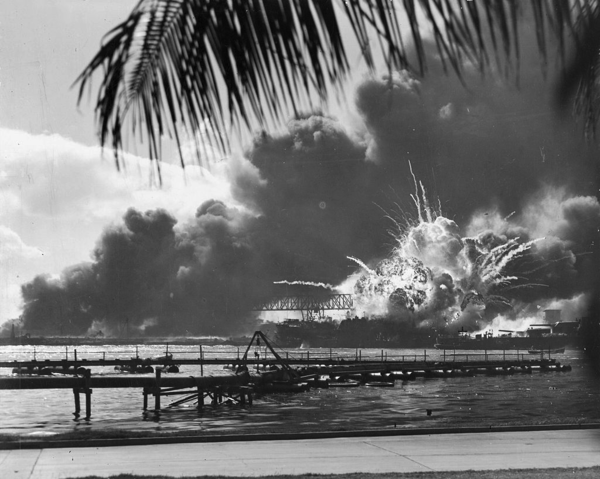
| 7 December | The American Pacific Fleet at Pearl Harbour got attacked by Japan. |
| 8 December | Britain and America declared war on Japan. |
| 11 December | Germany declared war on America. |
| 31 December | By this time, 53 merchant ships arrived in Russia and delivered 750 tanks, 800 fighter planes, 1,400 vehicles and 100,000 tons of general stores. |
See also: World War Two 1942
MLA Citation/Reference
"World War Two 1941". HistoryLearning.com. 2026. Web.