What was the Cold War?
What was the Cold War? The Cold War was a period of chronic hostility that existed between the Eastern Bloc (the USSR and its allies) and the Western Bloc (the United States of America, the United Kingdom, NATO and others). It gripped the western world from 1947 to 1991. The Cold War dominated international affairs for nearly half a century until the fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989 and the collapse of the Soviet Union.
At its core, the Cold War was caused by a clash of two antithetical ideologies: capitalism and communism. The Western bloc adhered to the capitalist ideology, whilst the Soviet Union was led by the communist party.
Note that the USSR came into being in 1922. As well as Russia, it included countries that now exist individually such as Ukraine and Georgia.

During World War Two, the US, the United Kingdom and the USSR were united against the common enemy of Nazi Germany. However, even during the war cracks were appearing in this relationship. One of America’s leading generals, Patton, even argued that the Allied army should unite with the remains of the Wehrmacht in 1945 and use its assets, such as the V2 rocket, to fight the oncoming Soviet Red Army. Winston Churchill was furious that Dwight Eisenhower, supreme head of Allied command, had allowed the Red Army to reach Berlin ahead of the Allied army. His anger was shared by Montgomery, a senior military figure in Britain.
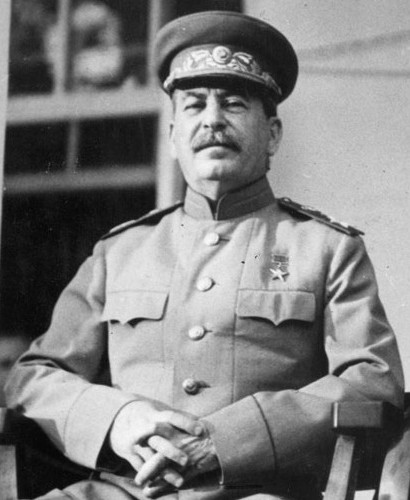
More seeds of distrust were sown when Truman hinted to Joseph Stalin, the Soviet leader, that America now possessed a new and terrifying weapon. Stalin only became aware of the full destructiveness of this weapon when reports of the dropping of the atomic bomb on Hiroshima got back to Moscow.
This was the situation after the war ended in 1945. Each side distrusted the other. The Soviets had the vast Soviet army occupying large swathes of Europe, whilst America possessed the most powerful weapon in the world, the Atomic Bomb.
What was the Cold War?
There are three types of war.
A Hot War is a situation of actual military warfare.
A Warm War is when talks are ongoing. There is a chance for a peaceful outcome but the opposing sides' armies and navies are being mobilised and war plans are being put in place ready for fighting.
A Cold War is a situation of tension and hostility between two opposing sides which does not disintegrate into open warfare. This term is most often used to describe the relationship between the Western and Eastern blocs between 1947 and 1991. The united States of America and the USSR never met in open conflict, but they indirectly fought in conflicts such as the Korean War and the Vietnam War.
The Cold War’ was arguably at its most dangerous during the Cuban Missile Crisis, when the ‘Cold War’ looked close to disintegrating into a ‘hot’ nuclear war.
Why was there so much enmity between these two super powers?
The Cold War was underpinned by several clashes in belief between the United States of America and the Soviet Union, which are summarised below.
| America | Soviet Union |
|---|---|
| Free elections | No elections or fixed |
| Democratic | Undemocratic/Dictatorship |
| Capitalist | Communist |
| Personal freedom | Society monitored by the secret police |
| Freedom of the press | Censorship |
The Cold War made the world a dangerous place for nearly 50 years. It encouraged the arms race, in which opposing sides stockpiled nuclear arms and competed to create more destructive weapons. By 1986, it is estimated that throughout the world there were 40,000 nuclear warheads. This was the equivalent of one million Hiroshima bombs.
See also: Causes of the Cold War in 1945
MLA Citation/Reference
"What was the Cold War?". HistoryLearning.com. 2026. Web.