Fedor von Bock
Fedor von Bock - nicknamed ‘Der Sterber’ or ‘the Dier’ - was a senior German Army officer during World War Two. Bock saw action in Poland, France and the USSR. Bock was a monarchist, and, though he fought loyally for Nazi Germany, had no truck with Nazisim.
Born on 3 December 1880, Bock served with distinction in World War One in the prestigious Fifth Regiment of Prussian Foot Guards. He was awarded the Pour le Mérite, Germany’s highest military decoration - this was unusual for a junior officer.
The Treaty of Versailles of 1919 severely restricted Germany’s military power but Bock remained in the army. During the 1920s he was part of a secret group which organised clandestine German rearmament and army training.
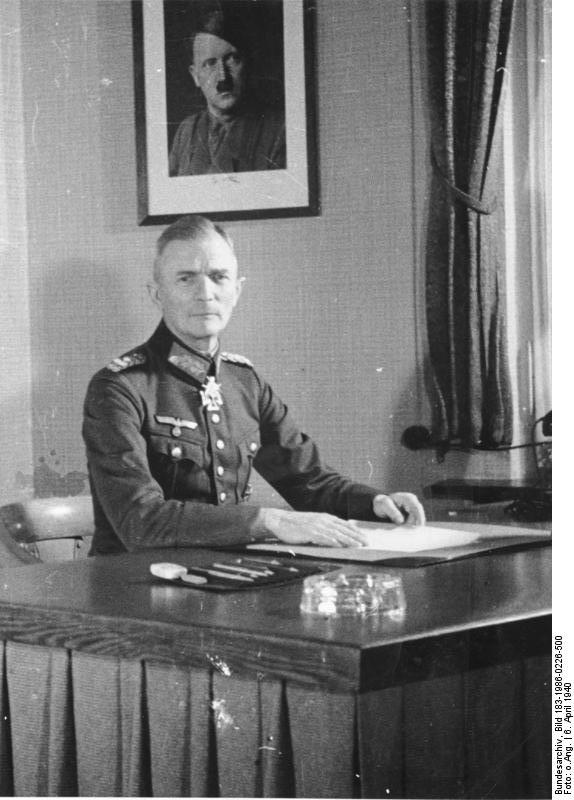

Bock was made commander of the Second Infantry Division in 1932 and then commander of the Third Army Group by Adolf Hitler in 1935, despite the fact that Bock remained an intransigent monarchist. Hitler apparently said that ‘Nobody in the world but Von Bock can teach soldiers to die’.
General von Bock led the Anschluss invasion of 1938 and the invasion of Czechoslovakia in 1939. He was Army Group North’s commander in the invasion of Poland on 1 September 1939. He then commanded Army Group B with distinction in the German attack on Western Europe. He was promoted to Field Marshal by Hitler off the back of these successes.
Bock was given command of Army Group Centre for ‘Operation Barbarossa’ – the attack on the USSR - on 1 April 1941. The Operation initially made rapid gains, but by winter the attack was stagnating. Bock did not succeed in taking Moscow, which was his main goal as commander of Army Group Centre. The Russian military had been denigrated for years in Germany and Hitler was infuriated by this failure. The Generals shouldered some of the blame. Bock was dismissed from his position as commander of Army Group Centre on 18 December 1941.
In January 1942 Bock commanded Army Group South. He was now 61, and in July of the same year he was included on the retired list. Days before the end of the war, on 4 May 1945, Bock, his second wife and her daughter were killed during an Allied air raid as they drove towards Hamburg.
See also: Omar Bradley
MLA Citation/Reference
"Fedor von Bock". HistoryLearning.com. 2024. Web.